What is bronchiectasis?
Bronchiectasis is an abnormal irreversible (permanent) dilatation of some bronchi or bronchioles (enlargement of parts of airway).
What are the causes of bronchiectasis?
The main cause of bronchiectasis is frequent, chronic lower respiratory tract infections like tuberculosis, haemophilus influenza, streptococcus, klebsiella etc. Bronchiectasis can occur as a complication of Cystic Fibrosis. A congenital (hereditary) condition called Kartageners syndrome where there is defect in ciliary function can also produce bronchiectasis.
What is the pathogenesis of bronchiectasis?
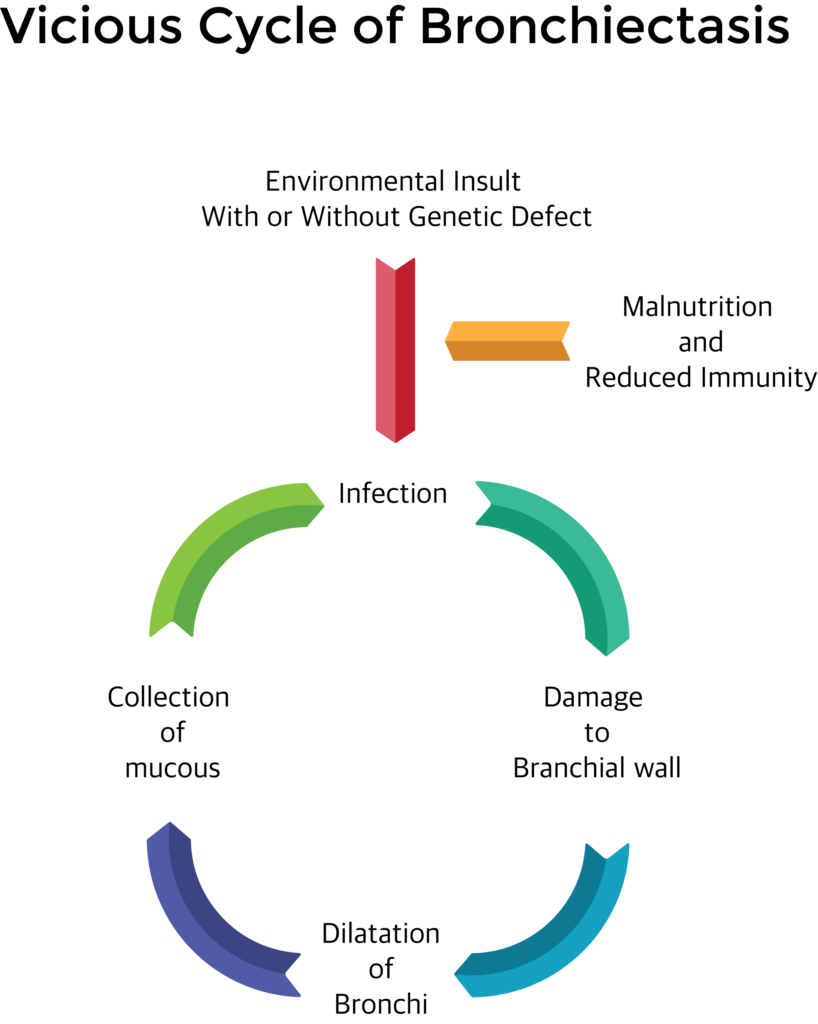
Chronic infections may damage the mucosal layer and mucociliary clearance. Inflammatory cells infiltrate leading to sloughing and ulceration in the wall of the bronchi. This may lead to patchy scarring and dilation of the area of bronchi. In the dilated area mucous gets collected which in turn gets infected and produce further damage.
What are the types of bronchiectasis?
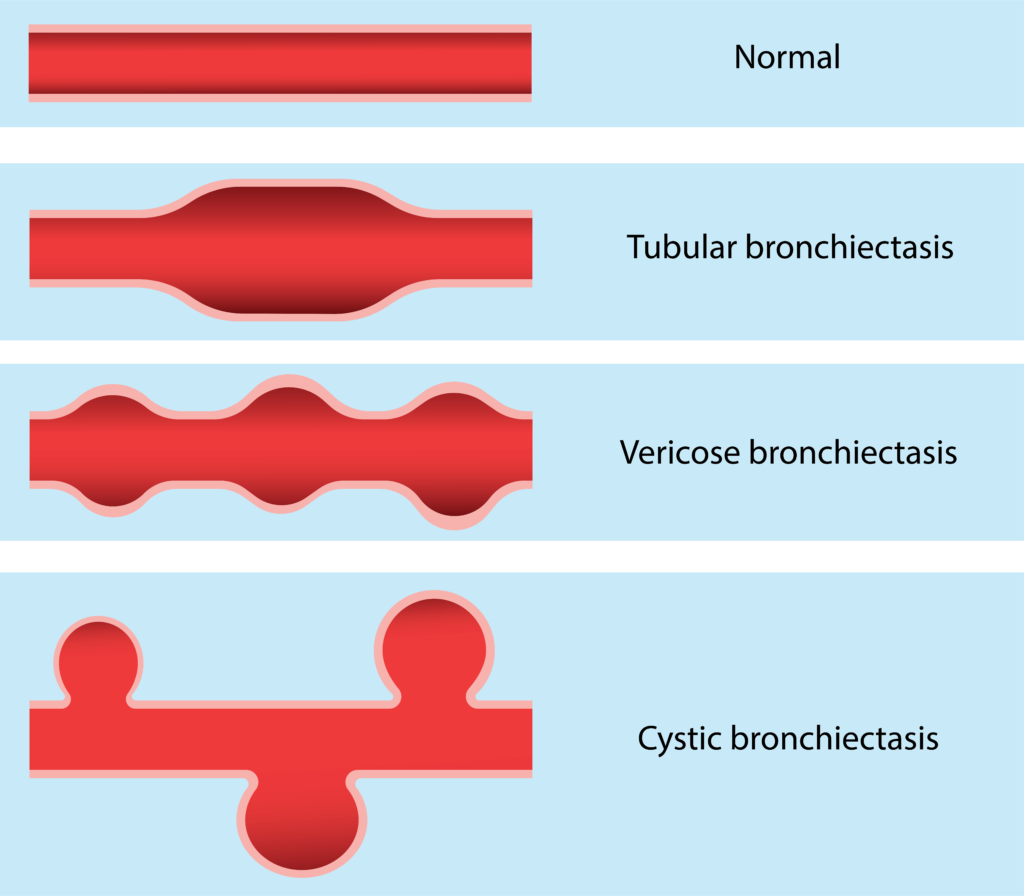
According to the shape of dilatation, there are three types of bronchiectasis. They are cylindrical, tubular and varicose.
What are the symptoms and signs of Bronchiectasis?
Symptoms
- Cough with copious (lots of), thick, foul smelling sputum.
- Haemoptysis (Blood in sputum)
- Shortness of breath, chest pain
- Fever with or without chills
Signs
- Halitosis (foul smelling breath)
- Labored breathing: patient using accessory muscles for breathing.
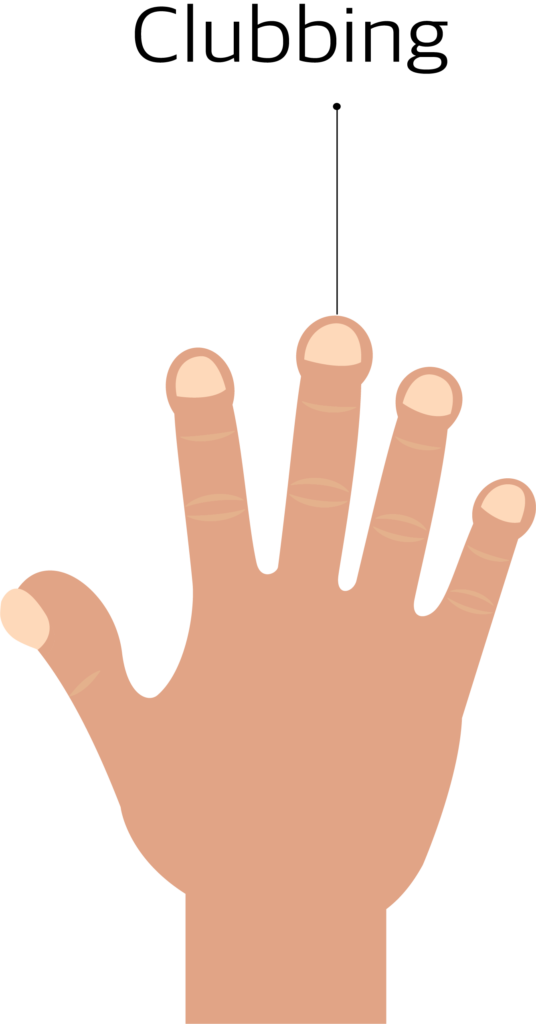
- Clubbing of fingers
- Coarse crackles (Crepitations) on auscultation.

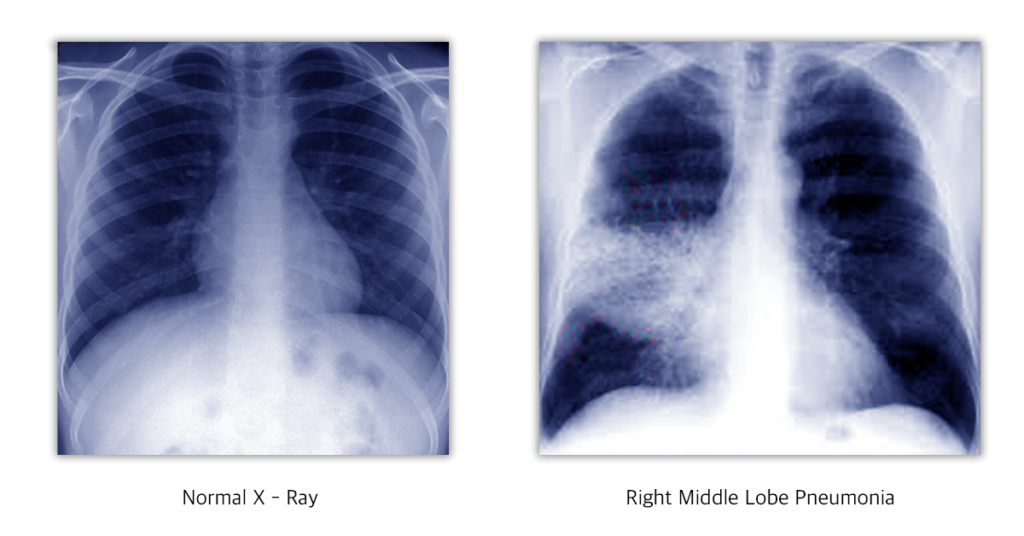
How to diagnose Bronchiectasis? (investigations)
X ray chest: increased bronchovascular markings, multiple cysts containing fluid levels.
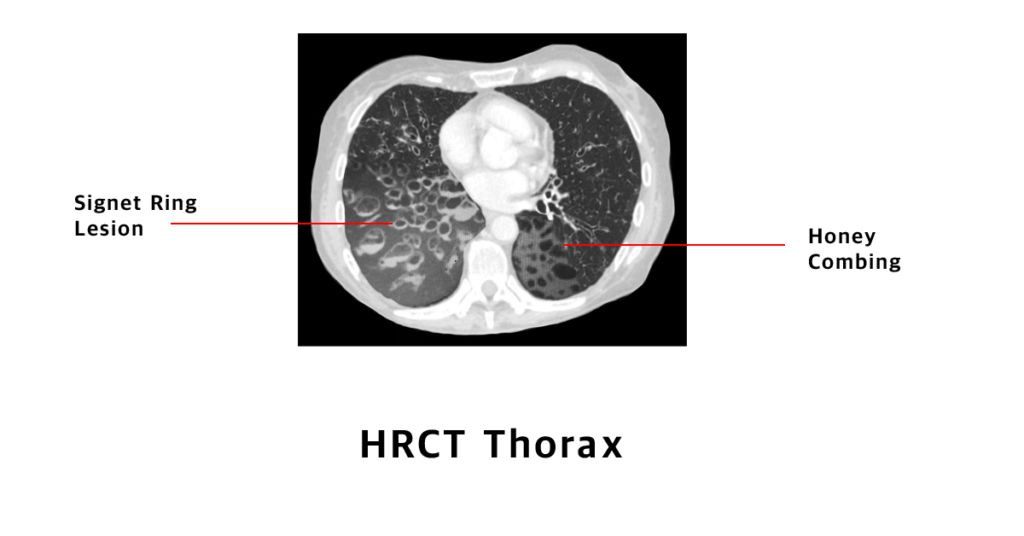
HRCT scan chest: Signet ring lesions, honey combing with fluid levels.
Sputum test for gram stain and acid fast stain.
Sputum for culture and drug sensitivity testing,
Routine blood tests like bloodcount, ESR, Bloodsugar,
Bronchography or bronchoscopy.
What is the treatment for bronchiectasis?
Postural drainage and chest physiotherapy.
Antibiotics: Start with broad spectrum antibiotics and can be changed according to the drug sensitivity.
Bronchodilators and expectorants,
Airway clearance devices,
Reassurance and health education.
Surgical excision: Very rarely done when bronchiectasis is localized and with severe haemoptysis.
How to prevent Bronchiectasis?
Diagnose and treat respiratory tract infections early.
Vaccinations schedule to be followed in children and adults can take pneumococcal vaccine like PISV 23 or PCV 13.
Prevent malnutrition by taking well balanced high protein diet.