What is Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis is a hereditary disease caused by gene mutation (alteration in gene sequence and structure). The mutation occurs in the gene for the CFTR protein (cystic fibrosis Trans membrane Conductance Regulator) on chromosome 7.
The main feature of Cystic Fibrosis is an abnormal high level of sodium and chloride in secretions of exocrine glands.
Cystic Fibrosis is seen in new born babies and seen in 1 in 2000 live births.
What are the organs affected by cystic fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis mostly affects the lungs. It can also affect secretory organs like sweat glands, digestive system, pancreas and liver.
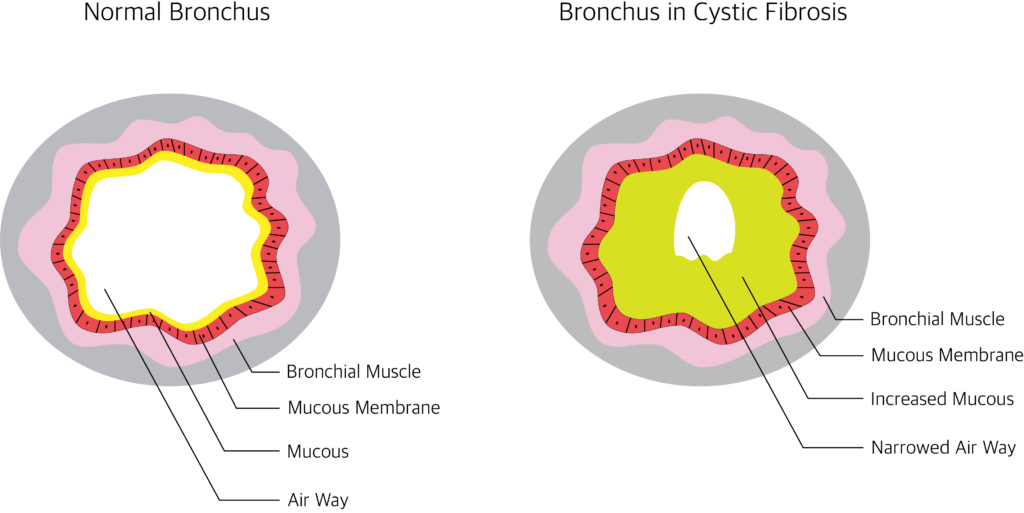
How Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs?
Because of the abnormal composition of sodium and chloride the mucus becomes thick and sticky. This impairs the mucociliary clearance. This leads to chronic infections and further leads to bronchiectasis, emphysema etc.
What are the signs and symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis?
Symptoms
Respiratory system
- Cough with sputum
- Wheeze
- Repeated lung infections
- Exercise intolerance
- Recurrent sinusitis
- Nasal polyps
Other organs
- Fatty liver or cirrhosis
- Diabetes
- Gall stones
- Intestinal obstruction
- Intussusception
- Infertility
Signs
In neonates: Meconium ileus, failure to thrive, rectal prolapse and distended abdomen.
In adults:
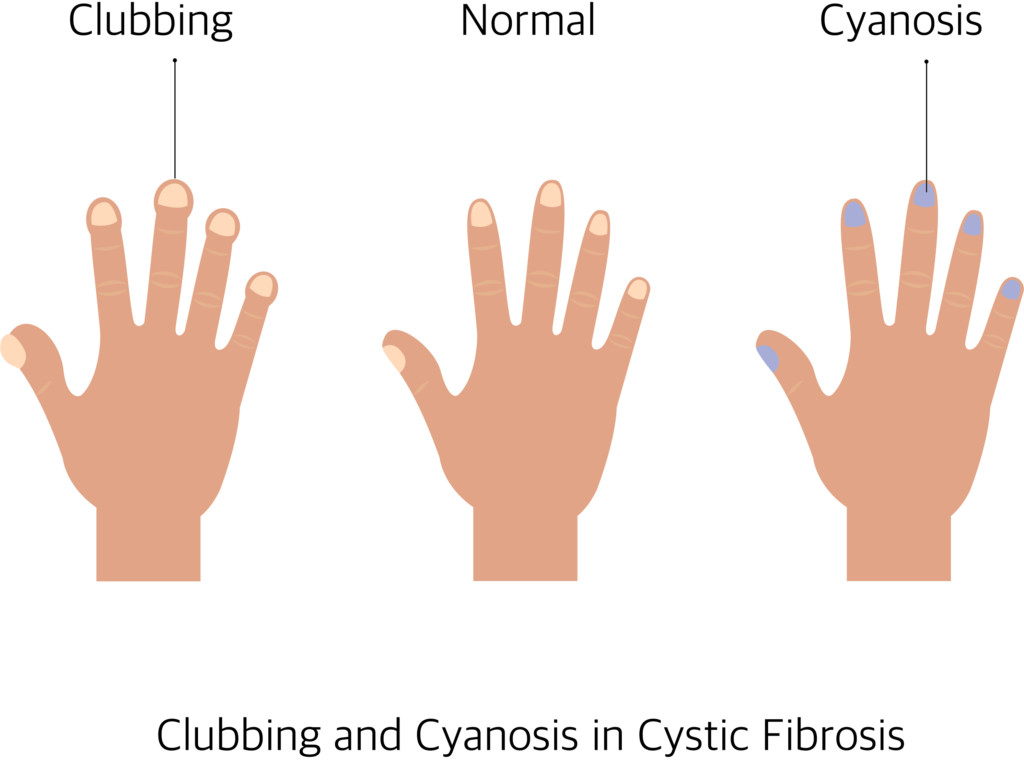
Clubbing: Tips of toes and fingers are enlarged.
Cyanosis: Bluish discoloration of nail, lips and tongue.
Bilateral coarse crackles heard over lung field.
How to diagnose cystic fibrosis?
- Sweat sodium and chloride test: It measures the salt in your sweat. The mean concentration of sodium and chloride in sweat is 20 to 35mmol/l. values above 70 mmol/l is suggestive of cystic fibrosis.
- Blood tests: Check the level of immune reactive trypsinogen (IRT) .The people with cystic fibrosis have higher level of immune reactive trypsinogen in their blood. Routine blood tests like blood sugar, liver function test, and kidney function tests are done.
- Sputum gram stain, culture and drug sensitivity testing.
- DNA test: To look for the mutations to CFTR Gene
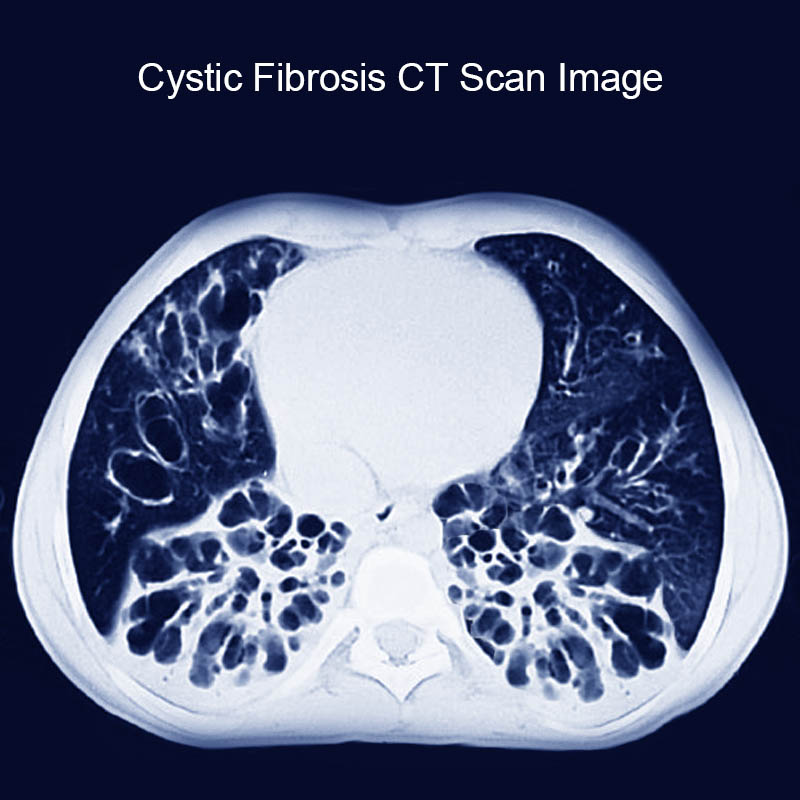
- Chest X ray and CT scan: Bronchiectasis or hyperinflation.
- Abdominal ultra sound scans to look for cirrhosis or fatty liver and chronic pancreatitis.
- Spirometry: Obstructive airway defect.
How to treat cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis cannot be cured completely. Treatment is aimed to reduce symptoms, slow down the progress of cystic fibrosis, prevent complications and to improve the quality of life.
Following treatments are given:
- Antibiotics
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (to prevent swelling)
- Bronchodilators
- Mucus thinner
- CFTR modulators
- Combination therapy
- Airway clearance techniques
- Oscillating devices
- PEP (positive expiratory pressure) treatment) using flutter or acapella PEP therapy.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation, Nutrition.
What are the complications ?
- Bronchiectasis (damaged airway)
- Haemoptysis ( blood in sputum)
- Pneumothorax
- Respiratory failure
How to prevent Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis can’t be prevented. Avoid marrying people with family history of Cystic Fibrosis. If parents have cystic fibrosis in their family, genetic testing can be done through amniocentesis (Remove fluid from the pregnant uterus) to rule out cystic fibrosis in the unborn baby. Genetic counselling before marriage is done to prevent producing babies with cystic fibrosis.
