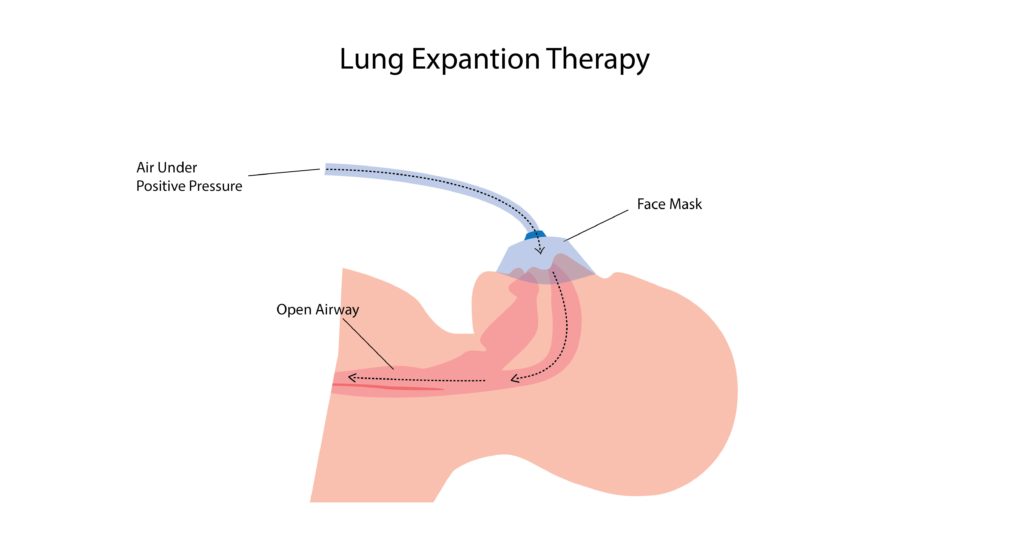
What is lung expansion therapy?
Lung expansion therapy includes many techniques to improve pulmonary function by increasing alveolar recruitment (open collapsed alveoli) and airway clearance. It increases lung volume by increasing the pressure difference between the alveolar space and pleural space (transpulmonary pressure).
Expansion of the collapsed lung can be obtained by deep breathing exercises or by applying positive pressure using devices like Incentive spirometer, CPAP, PEEP, Bi PAP, IPPB etc.
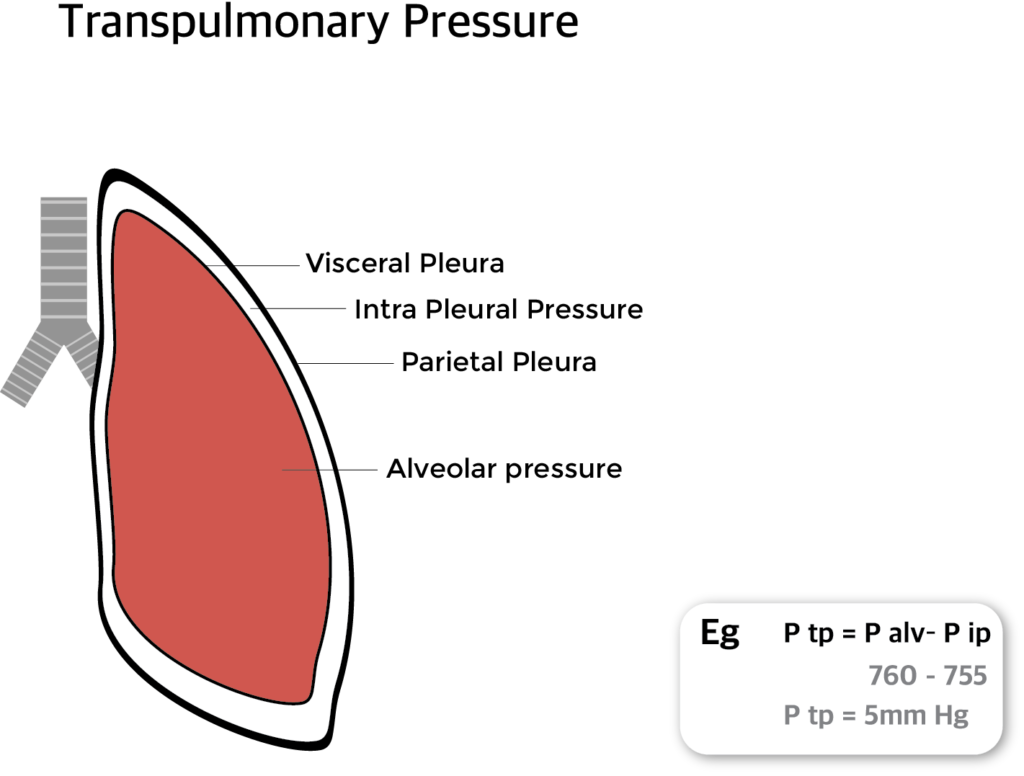
What is transpulmonary pressure?
Tran pulmonary pressure (P tp) is the difference between the alveolar pressure (P alv) and intra pleural pressure (P ip).
P tp = P alv– P ip
Transpulmonary pressure can be increased by
- Decreasing the surrounding pleural pressure
- Increasing the alveolar pressure
What are the indications for lung expansion therapy?
- Presence of alveolar collapse ( atelectasis)
- Conditions predisposing to atelectasis ( chronic bedridden patients)
- Upper abdominal or thoracic surgery
- Patients with neuromuscular disorders
- Sleep apnoea
- Surgery in patients with COPD
- Presence of restrictive lung disease.
What are the Contraindications for lung expansion therapy?
- Unconscious patients and un cooperate patients
- Patients who cannot understand and follow the instruction
- Patients unable to take deep inspiration, eg: Vital capacity <10 mL/kg or IC <1/3 predicted normal
What are the Complications Of lung expansion therapy?
- Hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis
- Discomfort due to inadequate pain control
- Barotraumas
- Hypoxemia (with interruption of therapy)
- Exacerbation of bronchospasm
- Fatigue
What are the techniques of lung expansion therapy?
Lung expansion therapy consists of a variety of respiratory care techniques designed to prevent or correct Collapse of lung (atelectasis).
The most common techniques include
- IIncentive spirometry (IS),
- continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
- positive expiratory pressure (PEP)
- Intermittent positive airway pressure breathing (IPPB)
These techniques help the patient to improve pulmonary function by increasing alveolar recruitment and airway clearance.
What is Incentive spirometer?
Incentive spirometer is a device which helps the patients to improve their lung function. The patient has to take a slow and deep breath, hold the breath for 5 to 6 seconds (sustained maximal inspiration) and then breathe out. This pressure helps to open the collapsed alveoli and airway.
What is IPPB?
IPPB (Intermittent positive pressure breathing) therapy is a technique used to expand the collapsed lung. Here inspiratory positive pressure is delivered in to the airway of a spontaneously breathing patient on an intermittent (short-term) basis by a trained respiratory therapist (RT). In IPPB a preset positive pressure is delivered only during the inspiratory phase of respiration.
This pressure helps the patient to take deep breath which in turn opens the collapsed lung and airway. IPPB is also used to improve cough mechanism, dislodge secretions and enhance delivery of inhaled medications.
Positive Airway Pressure Therapy
In positive airway pressure therapy compressed air in a preset pressure is delivered in to the airway which keeps the lung and airways open.
What are the types of Positive Airway pressure therapy?
- Positive expiratory pressure (PEP)
- Expiratory positive airway pressure (EPAP)
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
- Bi level positive airway pressure (Bi PAP)
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) Therapy
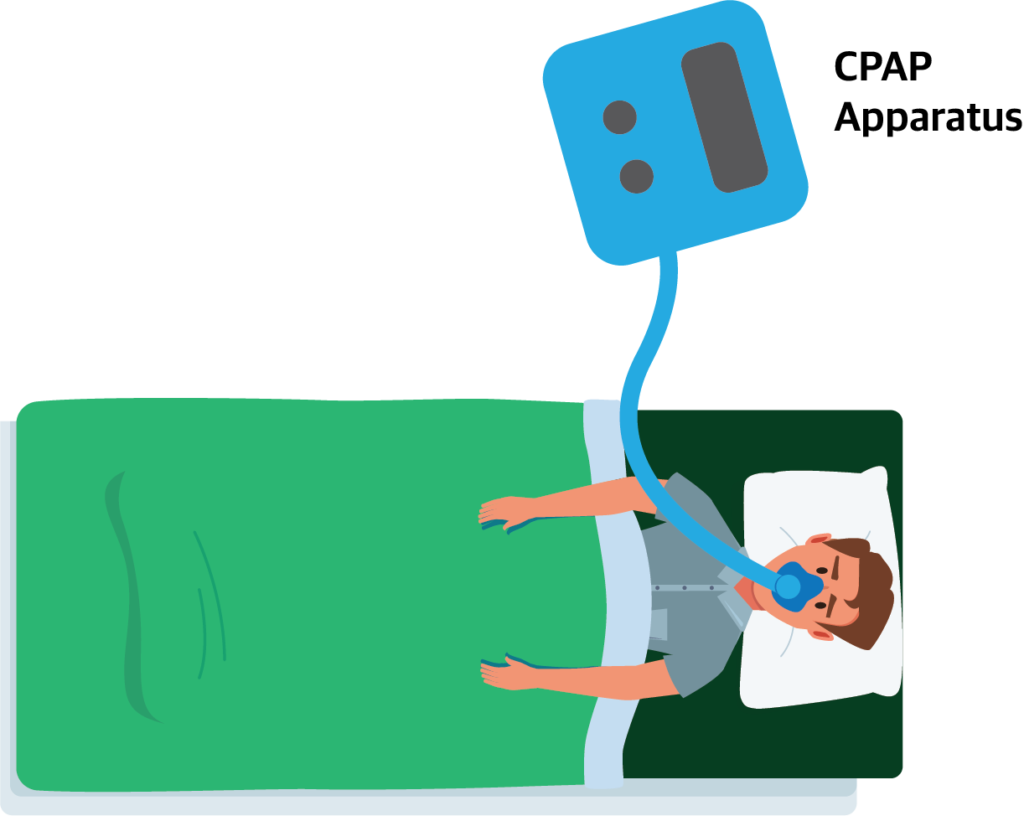
It is a positive airway pressure therapy where a preset continuous pressure is maintained in the airway throughout inhalation and exhalation thereby preventing collapse of alveoli and airways.
CPAP is mainly used in obstructive sleep apnoea.
Bi PAP (Bi level positive airway pressure) therapy
In Bi PAP therapy different level s of pressure are maintained during inspiration and expiration. Usually a pressure around 8 to 12 cm of water (H2O) is maintained during inspiration and pressure around 2 to 4 cm of H2O is maintained during expiration.
Bi PAP is a type of non invasive type of mechanical ventilator. It is usually used in patients with COPD and patients with respiratory distress and in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea patients where CPAP is not effective.
PEP therapy
In PEP (Positive Expiratory Pressure) Therapy the patient is made to breath out (Exhale) against resistance through a PEP device. The pressure created is transmitted to airways, creating a back pressure which prevents collapse and keep the airways open during exhalation.
PEP therapy prevents collapse of lung and airways, prolong expiratory flow and promote airway clearance.
Patient has to inhale, hold the breath and exhale through the PEP apparatus. A pressure around 10cm of water is maintained at mid expiration.
EPAP therapy
EPAP (Expiratory Positive Airway Pressure) therapy works by creating pressure during expiration and keeping the airway open until n inspiration. It is a simple, non invasive and effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnoea.
EPAP device consists of 2 two way valves one for each nostril. On inhalation the valves open and allow air to enter freely and on exhalation the valves restricts air flow. This restriction increases pressure inside the airway and prevents collapse of airway.
The EPAP device is small, portable, not attached to any machine and no need for power supply. Airway Pressure (EPAP) which is maintained until the start of the next inspiration.
