
What is Intubation?
Intubation ( Endotracheal Intubation ) is a process of placing a tube in the airway from the nose or mouth to trachea (wind pipe) to provide artificial respiration.
Who may need Intubation?
Intubation is done in patients with conditions such as respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, trauma etc.
Intubation is done in patients who cannot maintain a clear airway, who have severe airway obstruction and in patients who are unable to breathe on their own. It is also done to give general anesthesia and to start mechanical ventilation.
Intubation procedure must be carried out by well-trained medical professionals like doctors, respiratory therapists etc . Intubation is done in emergency conditions in ICU and operation rooms.
Equipments Needed
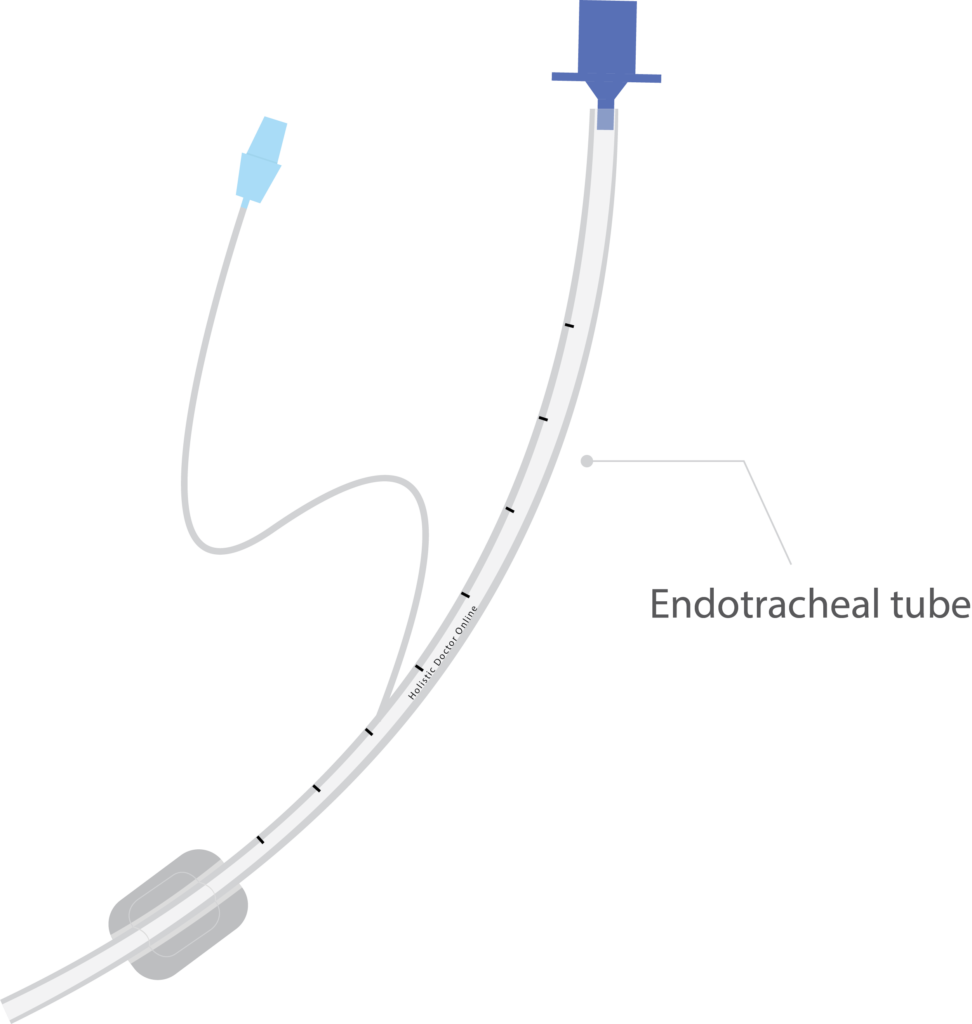
- Endotracheal tubes
- Laryngoscope with assorted blades
- Oxygen flowmeter and tubing
- Suction apparatus
- Flexible sterile suction catheters
- Sterile gloves
- Yankauer (tonsillar) tip suction
- Manual resuscitation bag and mask
- Colorimetric CO 2 detector
- Oropharyngeal airways
- PPE (gloves, gowns, masks, goggles or face shields)
- Laryngoscope with assorted blades
- Tongue depressor
- Stylet
- Stethoscope
- Tape or ET tube holder
- 10 or 20 ml syringe
- Water-soluble lubricating gel
- Magill forceps
- Local anesthetic spray
- Towels (for positioning the patients)

What preparation were done before intubation?
Before intubation the equipment’s must be checked and assembled. ET tube and laryngoscope must be selected according to patient’s size.
Before intubation ET tube must be checked for cuff leaks, it must be inflated and deflated with syringe. Bulb, blade, battery must be checked in the laryngoscope. Other equipment’s such as syringe tongue depressor, sty let, tapes, and Magill forceps must be checked and assembled.
Yankaeur suction can be used for oral suctioning. Vacuum pressure should be checked before suctioning. Suctioning is the process of applying negative pressure to remove the secretions and fluids in the airway. Before intubation patient should be 100% oxygenated with bag mask ventilation.
No intubation procedure must exceed 30 second. If intubation is not done within given with 30 second the oxygenation should be given with bag mask ventilation for 3 to 5 minutes.
In elective procedures, patients must be kept on fasting (no food or water) for a minimum period of 6 hours to prevent aspiration of food materials in to respiratory tract.
Premedication
For conscious patients sedation must be given to reduce anxiety. Patient is paralyzed to prevent resistance and to prevent vomiting. Local anesthetic is sprayed to numb the throat.
How intubation is done?
The medical professional doing intubation must stand behind the head of the patient. The patient must be in lying position. Sniffing position is done during the intubation; it is done by flexing the neck and tilting the head backward using hands. The sniffing position aligns patient’s mouth, pharynx and larynx in a same line and it opens the airway which helps in better visualization for the ET tube insertion.
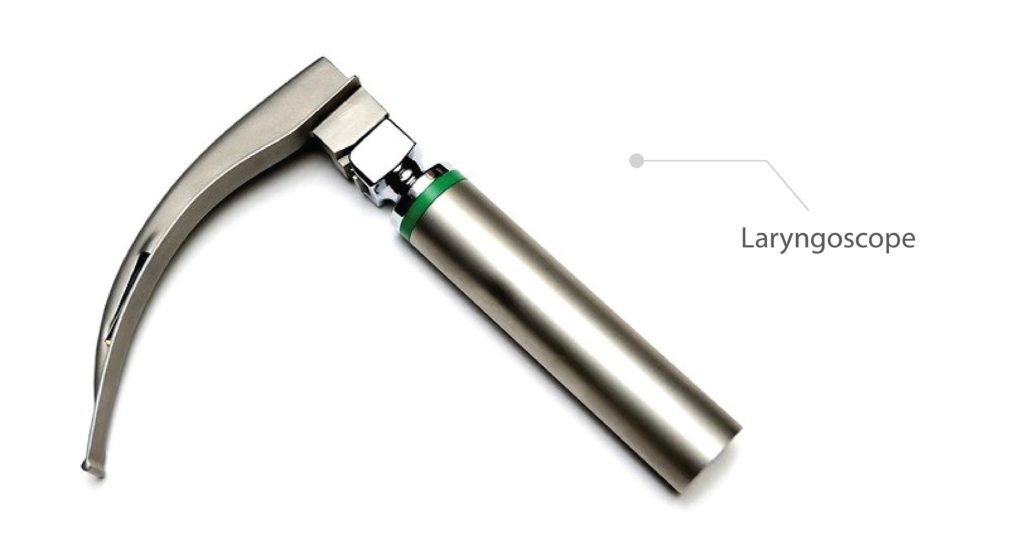
The laryngoscope is an instrument which contains a holder and blade. It helps in better visualization of larynx. It consists of two types of blade – Miller (straight blade) and Macintosh (curve blade).
The medical professionals must use left hand to hold the laryngoscope and the right hand to open the mouth and to insert the tube. The laryngoscope must be inserted from the right side of the mouth; the tongue must be displaced to the left. The laryngoscope must be preceded until the visualization of epiglottis.
The epiglottis must be moved for the insertion of ET tube. Moving the epiglottis gives better visualization of vocal cord where the ET tube is inserted. Epiglottis is present at the entrance of voice box; this prevents the entry of food particles into the wind pipe. It opens during breathing, cough and sneezing etc.
The curve blade is positioned at the base of the tongue the laryngoscope is lifted up and forward for moving of epiglottis. The straight blade is positioned posterior to epiglottis were the laryngoscope is lifted up and forward for moving epiglottis. If the glottis is visualized the ET tube must be inserted from the right side of the mouth. The ET tube should be passed inside the airway until the cuff enters the vocal cords.
Stylet must be used for a stiff placement of ET tube. ET tube is passed easily if water soluble jelly is applied over the tube. Once the ET tube is inserted in the airway laryngoscope and stylet must be removed.
The cuff should be immediately inflated with a 10ml syringe. The cuff helps to maintain the tubes position in the wind pipe and also prevents the entry of foreign particles into the lungs. The ET tube must be placed 3 to 6 cm above the tracheal bifurcation (division of trachea).
Methods to check the position of endotracheal tube
Chest wall movements – After ET tube placement bag mask ventilation should be done. If bilateral chest wall movement is observed the ET tube is located above the carina. If abdominal bloating is observed, the ET tube is placed in the food pipe and re intubation should be done in this condition.
Bilateral lung sounds – Auscultation is done to check the bilateral lung sounds. If no lung sound isobserved in the left lung the ET tube is placed the right main bronchus. In this condition the ET tube must be slightly pulled out. If there is absence of lung sound the ET tube is in the food pipe. Reintubation should be carried out.
Bronchoscopy: This procedure shows the accurate position of the ET tube.
Capnometry: It is the measurement of CO 2 in the exhaled air. Normal PCO 2 in the exhaled air is 35 to 45mm of hg. If less amount of CO 2 is indicated the ET tube is in food pipe and re intubation should be done in this condition.
Chest x-ray: The radiograph line present in the ET tube shows the position of ET tube in the airway.
Tube length: The length marking present in the ET tube is used to determine the positioning. The tube length from the teeth to the tip is used to rule out the depth of the ET tube in the airway.
After confirmation of the ET tube placement in the airway it is held in position with tapes or tube holder. Oropharyngeal airways are placed to prevent the tongue fall back & to prevent the biting of tube. Then the ET tube is connected to the ventilator.
How to remove ET tube?
When the patient is weaned from mechanical ventilator and the patient cab breath on his own, ET tube can be removed. The adhesive tape holding the ET tube to the face is removed, the cuf of the Et tube is deflated and the ET tube is slowly pulled out.
What are the complications of Intubation?
Intubation can produce tissue damage, bleeding, improper placement leading to cerebral ischemia and brain damage. It can damage the larynx and vocal cord and produce speech problems. Intubation can also produce tracheal stenosis, tracheooesophageal fistula, pneumothorax, atelectasis and infection.

It’s very useful sir good job👍