What is pulmonary Interstitium?
The Pulmonary Interstitium is the anatomical space between the alveolar epithelial cells and the endothelium of the pulmonary capillaries. It continues as the space surrounding the bronchi and blood vessels. The interstitium contains perivascular and peri lymphatic tissue.
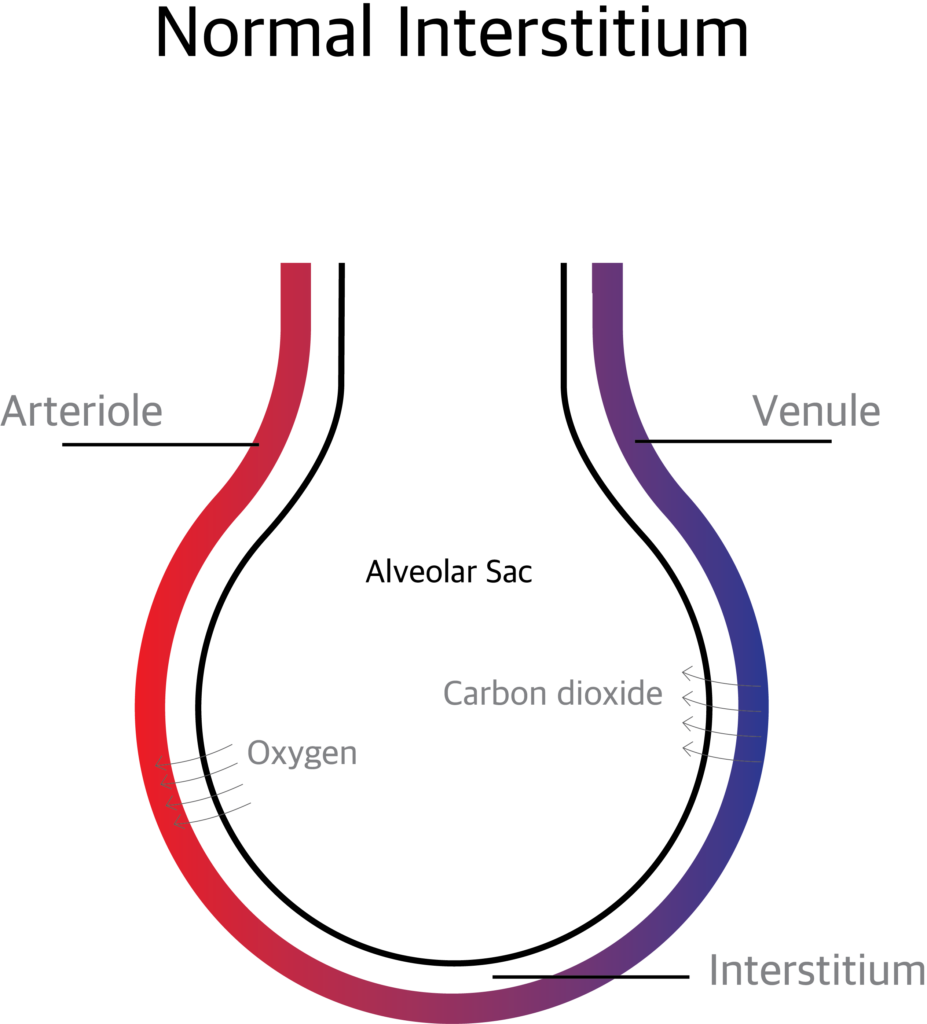
What are the sub divisions of Pulmonary Interstitium?
The pulmonary interstitium is divided in to 3 components.
The Axial (peri bronchovascular) Interstitium: The space around the airways and the pulmonary artery.
The Parenchymal or Alveolar Interstitium: The interstitium supporting the gas exchanging part of the alveoli.
The Pheripheral or Sub pleural Interstitium: The space between the parenchyma of lung and the visceral pleura.
What are the functions of pulmonary Interstitium?
The pulmonary Interstitium supports the alveolar sacs and transport nutrients. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place through the pulmonary interstitium.
The gas exchange is affected when excess extra vascular fluid accumulates in the interstitium or when the interstitium is affected by inflammation and scaring.
Disorders of pulmonary Interstitium ( Interstitial lung disease)
What is Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)?
Interstitial lung disease is a collection of more than hundred disorders affecting the pulmonary Interstitium.
What is the pathophysiology of Interstitial Lung Disease?
Normally when there is an infection and inflammation, the interstitium will heal shortly with minimal or no scaring. Repeated insult and infection over times makes the interstitium thick and hard. This hardened interstitium becomes a barrier between the alveolar membrane and blood vessels thereby preventing gas exchange.
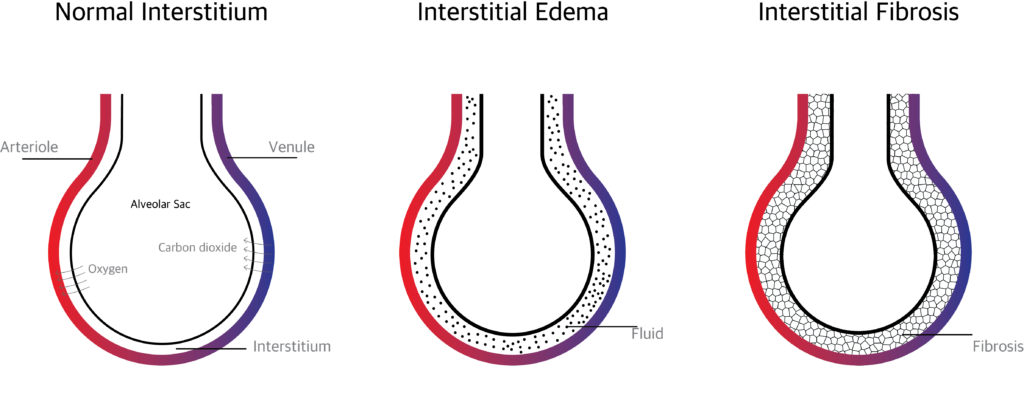
What are the causes of Interstitial Lung Disease?
There are more than hundred causes. The causes may be known, unknown or hereditary.
Known Causes:
- Granulomatous infections (like tuberculosis, mycoplasma), viral and fungal infections can cause interstitial lung diseases.
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis:- Dust, molds, animal or birds proteins (Feathers or droppings) can irritate and produce scarring of the interstitium.
- Pneumoconiosis:- occupational hazards like breathing asbestos fibers (Asbestosis) or Silica dust (silicosis), cotton fibers (byssinosis) Sugarcane fibers and mold (bagassosis) etc can cause ILD.
- Toxic pneumonitis:- Inhaling chemicals, fumes or drugs can develop ILD. Exposure to radiation can also produce ILD.
- Drug induced:- Ingesting drugs like Nitrofurantoin, bleomycin, propranolol, amiodarone and rituximab can cause ILD.
- Malignancy:- Neoplasms like bronchoalveolar cell carcinoma and lymphangitic carcinomatosis can produce ILD.
- Respiratory bronchiolitis:- caused by chronic smoking can also produce ILD.
Unknown causes:
- Crptogenic Organizing pneumonia:- otherwise called as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP)
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Sarcoidosis:- involves lymph glands, other organs like skin heart etc, and interstitium.
- Langerhans cell histocytosis
- Eosinophilic pneumonia
- Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- Pulmonary vasculitis;- Eg: wegener’s granulomatosis.
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- Connective tissue diseases like Rheumatoid Arthritis, Progressive systemic Selerosis etc…
Inherited (hereditary) causes:
- Neurofibromatosis
- Tuberous sclerosis
- Metabolic storage disorder
- Hypocalciuric hypercalcemia
- Hermanszky-pudlak syndrome
What are the signs and symptoms of Interstitial Lung Disease?
Symptoms:
The main symptom is gradually increasing breathlessness on exertion and finally breathlessness even at rest.
Cough usually dry, weight loss, general weakness and fever when there is super added infection.
Signs:
Digital clubbing,
Velcro crackles on auscultation.
How to diagnose ILD?
Detailed history regarding occupation, exposure to dust, chemicals, drugs, family history, and personal history (smoking, drugs etc) has to be taken. In ILD is suspected the following investigations have to be done.
What are the tests (investigations) done in interstitial lung disease?
- Routine investigations like complete blood count, ESR, Blood sugar etc were done.
- Serological tests like Antinuclear Antibody Test, Creatine Kinase, Rheumatoid Factor etc… are done to rule out connective tissue diseases.
- X- Ray chest
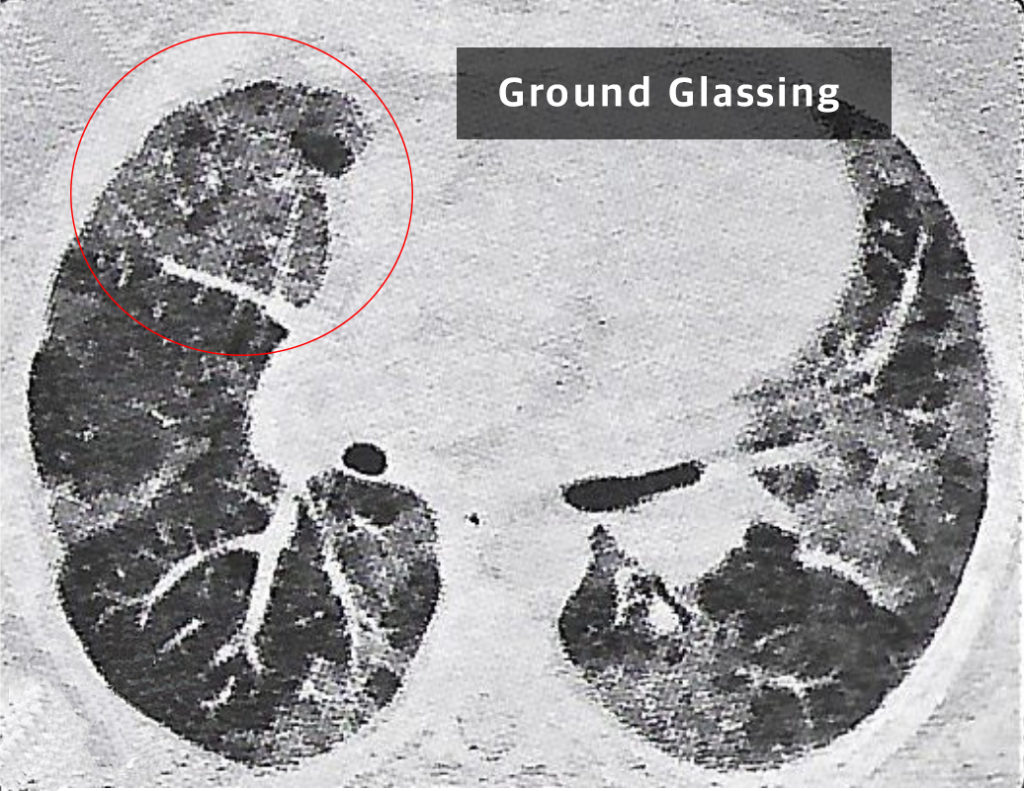
- HTCT thorax: Patchy peripheral opacities are seen. Bronchiectatic changes and sub plural reticular opacities seen. Limited ground glass opacities are seen.
- Sputum examination, culture and sensitivity testing
- Spirometry: Restrictive pattern
- Six minutes walk test bronchoscopy and broncho alveolar lavage: specimen sent for cell count, cytology, culture etc.
- Lung Biopsy: Trans bronchial biopsy (TBLB) or Video assisted thoracoscopic biopsy (VATS)
What is the treatment for interstitial lung disease?
Treatment is based on the diagnosis. If due to known cause treat the cause.
If the cause is not known, the goal of the treatment should be to reduce symptoms, to improve the quality of life and to reduce complications.
Response of treatment varies. Some may recover well and some may not.
The treatment options are:
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids like prednisone reduce inflammation. Oral Steroids are initially used to reduce inflammation but in later stages steroids may not be effective.
- Immunosuppressive drugs: Azathioprim or Cyclophosphamide or Mycophenolate can be given when steroids are not effective.
- Antifibrotic agents: Pirfenidone, Colchicine, D-pencillamine, Interferon Y or B, Suramin, Nintedanib etc can be given to reduce scarring.
- Antioxidants: N-acetyl cystein, Niacin, Glutathione, etc can slow down the progress of the disease.
- Long term oxygen therapy: Some people may need long term oxygen therapy. Oxygen concentrator can be advised.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Pulmonary rehabilitation given to the patient to make him live independently in the society. Pulmonary rehabilitation includes health education, exercises, breathing techniques, occupational therapy, counselling and psychosocial support.
- Lung Transplant: In end stage ILD, when other treatment options are not effective lung transplant can be tried.
