What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is the inflammation of the lung parenchyma ( tissue that involves in gas exchange in the lungs otherwise called alveolar tissue ). When inflammation is caused by infection it is called pneumonia and when inflammation is caused by other causes like radiation, inhalation of chemicals etc… it is called as pneumonitis.
What are the causes of pneumonia?
Pneumonia can be caused by infection, inhalation of chemicals and gas or by aspiration of foreign bodies.
What happens to the lung in pneumonia? (Pathology)
- Stage of congestion
There is vascular engorgement and the intra-alveolar spaces are filled with fluid, blood cells and bacteria. - Stage of red hepatization
Exudates develops and the area is filled with pus and blood and the area becomes firm like liver. - Stage of grey hepatization
Slow disintegration of red cells and fibrin exudates forms. - Stage of Resolution
The thick exudates undergo enzymatic digestion. The debris are removed by macrophages and coughed out. It may heal fully of fibrosis occur.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
- Cough: Dry or Productive with sputum.
- Fever: with rigor (chills)
- Difficulty in breathing (shortness of breath)
- Fatigue
- Cyanosis (bluish coloration of tongue lips ect)
How Pneumonia is classified? – Types of pneumonia
Pneumonia can be classified according to
1. The anatomical site involved
- Eg: Bronchopneumonia, Lobar pneumonia.
2. The Source of infection
Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
- Eg: Infection acquired from the society.
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) – Nosocomial Pneumonia
- Pneumonia acquired from the hospital and manifesting after 48 hours after admission.
Ventilator Acquired Pneumonia (VAP)
- Appears 48 hours after starting mechanical ventilation.
Health Care Associated Pneumonia
- Pneumonia acquired from health care personals when the patient took out patients treatment or while undergoing procedures like dialysis, dressing, IV fluids etc…
3. The organisms causing
Bacterial
- Streptococcus pneumonia, Staphylococcus pneumonia.
Viral
- H1N1 pneumonia, COVID 19 Pneumonia.
Fungal
- Coccidioidomycosis
Chemical
- Infection after inhalation of gas or acid fumes.
Aspiration
- Infection after aspiration of stomach acid, water etc…
Investigation For Pneumonia
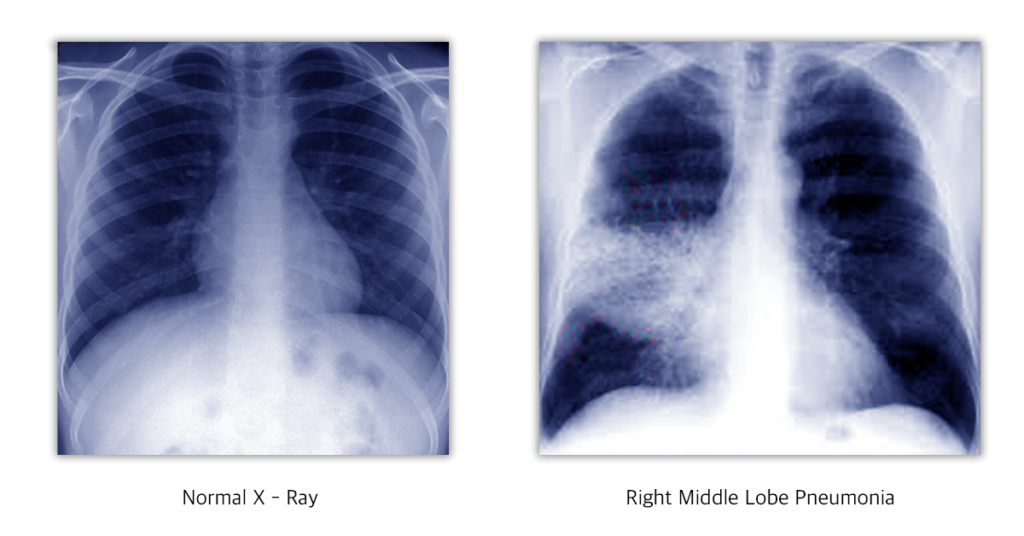
X-ray Cheat, HRCT Thorax, Sputum examination: Gram stain and AFB stain, Sputum culture and sensitivity, Blood culture, Serological tests for viral infection and to rule out HIV infection, Routine investigations like CBC, blood sugar, urea and creatinine.
How to assess the Prognosis?
Prognosis can be assessed using CURB-65 scoring system.
One point is given for each.
C – Confusion
U – Urea: more than 7 m mol/L
R – Respiratory rate: more than 30/ minute
B – Blood pressure: less than 90 systolic and/ or 60 diastolic.
65 – Age above 65.
Severity
If the total score is
0 to 1 – Mild outpatient treatment is enough.
2 – Hospital admission necessary.
3 to 5 – Severe, intensive treatment necessary, the death rate increases as the score.
Treatment For Pneumonia
Mild patients can be treated as outpatients with oral antibiotics and antipyretics. Moderate and severe patients need injections and intravenous fluids with oxygen support. Severe patients may need mechanical ventilation.
Broad spectrum antibiotics are started and later on altered according to the culture and sensitivity report.
Fever, body pain and other symptoms can be treated accordingly.
Prevention
Pneumococcal vaccine (like 23 valent pneumovax) can be given to vulnerable people like senior citizens over 65 years, diabetics, patients with pre existing lung disorders or patients on immunosuppressant drugs.





This is very useful for me
I need more knowledge about respiratory conditions and want more