What are Sleep disorders?
Sleep Disorders are a group of conditions producing changes in the ability of a person to sleep well on regular basis.
Sleep disorders can affect the overall health of the person, his quality of life and safety of the person while driving or working in daytime.
What are the uses of sleep?
People spend more than one third of their life sleeping. Sleep allows our brain and body to rest and repair itself.
Sleep help in growth, improves memory, synthesize hormones, reduces stress, boost immunity, reduces inflammation, maintains healthy blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and prevent cancer.
What are the types of Sleep disorders?
Insomnia:
This is the most common sleep disorder. Here the person develops difficulty in falling asleep and maintaining quality sleep.
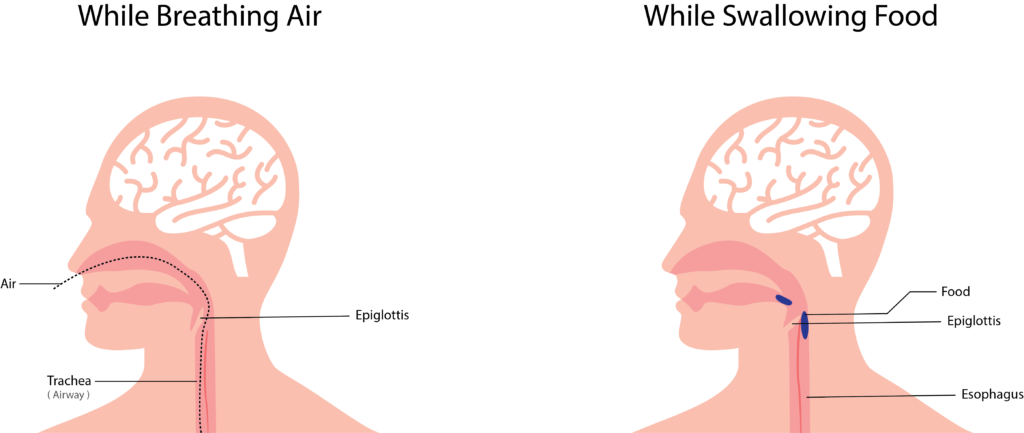
Sleep Related Breathing Disorders (Sleep Apnea):
Here the person develops abnormality in breathing while sleeping. Common sleep related breathing disorders are
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Obstructive Sleep Apnea is the most common sleep apnea. In OSA the person’s throat muscles relax and obstruct the airway during sleep. OSA is common in obese people.
- Central Sleep apnea: Central Sleep apnea is due to lack of signals from brain to breathe while the person is sleeping. Central Sleep apnea is normally due to an underlying medical condition like stroke, high blood pressure, heart failure, drug induced etc.
- Mixed: combination of central and obstructive sleep apnea.
- Isolated variants:
Snoring: Harsh vibratory sound produced, when air passes through relaxed tissues of throat. Snoring can also occur in sinusitis, enlarged tonsils, cold, and in obesity.
Catatherenia: Moaning or groaning sound produced during expiration.
Hypersomnlence:
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a condition where the person has excessive, uncontrollable sleepiness in daytime. May fall asleep at inappropriate times ( like while driving or at work)
- Hypersomnia: In hypersomnia the person has difficulty in staying awake in daytime even after a good night sleep. They may nap often but naps are not refreshing.
Parasomnias:
In parasomnia the person may have unwanted physical actions or experiences during sleep.
E.g.: Sleep walking, sleep talking, sleep terrors, sleep enuresis and nightmare disorder.
Sleep Related Movement Disorders:
The person may have simple and repetitive movements during sleep.
E.g.: Restless leg syndrome, Periodic limb movement disorder and sleep bruxism.
Circadian Rhythm Sleep Wake Disorder:
Here the person may have desynchronization between his internal clock (sleep wake cycle) and light darkness cycle.
E.g.: Jet lag disorder and Shift work disorder.
What are the Symptoms of Sleep disorders?
Symptoms depend on the type of disorder. The person may take long time to sleep, may wake up frequently and may have difficulty in going back to sleep. May be drowsy and fall asleep at daytime. Snore and may stop breathing often during sleep. Move or jerk their arms and legs during sleep.
How Sleep Disorders are Diagnosed?
- History: Detailed history taken from the patient, family members and bed partner.
- Sleep Questionnaires or Sleep Scale can be used
- Clinical Examination: complete clinical examination including weight, blood pressure, and ENT examination done.
- Routine blood investigations including ABG done. X-ray chest and HRCT thorax taken if necessary.
- Sleep studies:
- Polysomnography
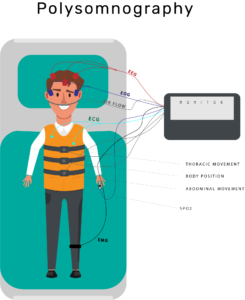
Polysomnography is the common sleep study done. It is done in a sleep lab or home. The person is made to sleep and activity of brain (EEG), oxygen saturation, Muscle movements (EMG) abdominal and leg movements, oral and nasal air flow and eye movements are recorded. Number of apnea and hypopnea are recorded.
- Multiple Sleep Latency Test:
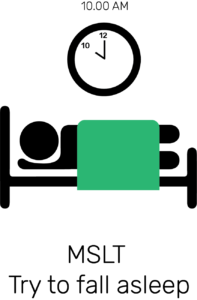
MSLT is usually done in day time after polysomnography test. This test shows how quickly a person can fall asleep. In daytime the person is asked to lie down and try to sleep. Each nap time is 20 minutes. If the person sleeps he is awakened after 15 minutes. Test repeated after 2 hours, like that 5 tests are done in that day. Time of light out and sleep onset is called sleep latency Usually done to diagnose narcolepsy and hypersomnia.
Below 5 minutes – Sever sleepiness
5 to 10 minutes – Moderate sleepiness
10 to 15 minutes – Mild sleepiness
- Maintenance of Wakefulness Test:
In MWT how well a person is able to stay awake is tested. In a dark, quit and comfortable room the person is asked to stay awake and not to fall asleep. MWT is also done after overnight polysomnography. Here also 20 minutes slots are given repeated every 2 hours.
- Actigraphy: Actigraphy is a small device worn like a wrist watch for days together. It records the movements of the person, sleep wake cycle, circadian rhythm etc.
What is the treatment for sleep disorders?
- Good sleep habits
- Life style changes with healthy diet and regular
- exercises.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy to reduce anxiety
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy.
- Sleeping pills,
- Melatonin Supplements,
- Treatment of under lying cause,
- Breathing devices,
- Dental guard,
- Surgery.